The primary function
of cable is to carry energy reliably between source and utilization equipment.
In carrying this energy there are heat losses generated in the cable that must
be dissipated.
The cable sizing
procedure is based on the following considerations:
Full
load current shall be calculated from following formula :
For AC systems, the formula of calculating full load current:
Ifl = P / V . cos
where:
P : Active Power (W)
V : Voltage (V)
Ifl : Full
load current (A)
η : Efficiency
For DC systems, the formula of calculating full load current:
Ifl = P/V
The minimum conductor size, before the application
of any adjustment or correction factor, shall have an allowable ampacity 125%
of full load current.
Df =k1 x k2
a.
Temperature Derating Factor (k1)
Temperature derating factor cable
are considered as 1.00 base on NEC Table 310.15(B)(2)(a) for maximum conductor
temperature 900C and ambient temperature 260C - 300C
b. Group
Derating Factor (k2)
Group derating factor cable
are considered as 80% base on NEC Table EC Table 310.15 (B)(3)(a) for number of
current carrying conductor 4-6
Over all derating factor
based on above consideration to be used on the corrected cable ampacity (cable
ampacity at 200C) shall follow
For AC systems, the method of calculating voltage drops based on load
power factor is commonly used. Full load currents are normally used, but if the
load has high startup currents (e.g. motors), then voltage drops based on
starting current (and power factor if applicable) shall also be calculated.
where
VD3φ : Three phase voltage drop in Volt
L : Length of cable in meter
I : Load current in ampere (RMS
Value)
R : Resistance of cable in ohms
per kilometer
X : Reactance of cable in ohms per
kilometer
Cos
θ : Power factor of connected load
V : Nominal system voltage (line
to line)
n : Number of cable in parallel
per phase
where
VD1φ : Single phase voltage drop in Volt
For
DC system is calculated using the following
formula:
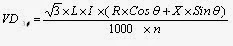


Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar